As threat management gateway takes center stage, this opening passage beckons readers into a world crafted with good knowledge, ensuring a reading experience that is both absorbing and distinctly original.
Threat management gateway (TMG) is a critical component of any organization’s network security infrastructure. It provides a comprehensive suite of security features that can help to protect against a wide range of threats, including malware, viruses, and hackers.
Threat Management Gateway (TMG) Fundamentals
A Threat Management Gateway (TMG) is a network security device that monitors and controls incoming and outgoing network traffic. It acts as a firewall, intrusion detection system, and intrusion prevention system, providing comprehensive protection against a wide range of cyber threats.
TMGs can detect and mitigate various threats, including:
- Malicious software (malware), such as viruses, worms, and Trojans
- Network attacks, such as denial-of-service (DoS) and man-in-the-middle (MitM) attacks
- Data breaches, such as unauthorized access to sensitive information
Implementing a TMG in an organization’s network offers several benefits, including:
- Enhanced network security by blocking malicious traffic and preventing unauthorized access
- Improved network performance by optimizing traffic flow and reducing latency
- Increased compliance with industry regulations and standards
TMG Deployment and Configuration

Deploying and configuring a Threat Management Gateway (TMG) is crucial for establishing a secure network infrastructure. TMG offers comprehensive protection against a wide range of cyber threats, including malware, phishing, and unauthorized access. This guide provides a step-by-step approach to deploying and configuring a TMG, ensuring optimal performance and protection for your network.
Deployment
To deploy a TMG, follow these steps:
- Hardware Requirements:Determine the hardware requirements based on the size and complexity of your network.
- Network Topology:Design the network topology to accommodate the TMG as a gateway or inline device.
- Installation:Install the TMG software on the designated hardware.
- Network Configuration:Configure the network settings, including IP addresses, subnet masks, and default gateways.
Configuration
Once deployed, configure the TMG to meet your specific security requirements:
- Firewall Rules:Define firewall rules to control inbound and outbound traffic, allowing or blocking specific protocols and ports.
- Network Address Translation (NAT):Configure NAT to translate private IP addresses to public IP addresses for external access.
- Web Filtering:Implement web filtering policies to block access to malicious or inappropriate websites.
- Intrusion Prevention System (IPS):Enable IPS to detect and block known attack patterns.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN):Configure VPN to provide secure remote access to the network.
Optimization
To optimize TMG performance, consider these best practices:
- Hardware Sizing:Ensure the TMG hardware meets the demands of your network traffic volume.
- Regular Updates:Keep the TMG software and firmware up to date to address security vulnerabilities.
- Monitoring and Logging:Monitor TMG logs to identify potential threats and performance issues.
- Load Balancing:Implement load balancing to distribute traffic across multiple TMG devices for increased capacity.
- Redundancy:Configure redundant TMG devices to ensure failover and maintain network availability.
TMG Management and Monitoring
Effective management and monitoring are crucial for maintaining the optimal performance and security of a Threat Management Gateway (TMG). Various tools and techniques can be employed to accomplish this, ensuring the TMG operates efficiently and securely.
The threat management gateway serves as a critical safeguard, protecting your network from malicious threats. However, even with robust security measures in place, our furry companions may experience pain and discomfort. For those seeking guidance on pain management for their canine friends, I recommend exploring this comprehensive resource: pain management for dog . By understanding the principles of pain management, we can ensure the well-being of our beloved pets while maintaining a secure threat management gateway.
Monitoring Tools
- TMG Management Console:Provides a centralized interface for configuring, monitoring, and troubleshooting TMG.
- Event Viewer:Logs system events, including security events, providing insights into potential issues.
- Performance Monitor:Monitors system performance metrics, such as CPU and memory usage, to identify performance bottlenecks.
- Third-Party Monitoring Tools:Specialized tools offer advanced monitoring capabilities, such as real-time alerts and detailed reporting.
Troubleshooting Common Issues, Threat management gateway
- Connection Problems:Verify network connectivity, firewall settings, and TMG configuration.
- Performance Issues:Monitor system resources, optimize TMG settings, and consider hardware upgrades.
- Security Breaches:Review event logs, check for unauthorized access, and update security policies.
- Software Updates:Regularly apply TMG software updates to address vulnerabilities and improve functionality.
Importance of Security Audits
Regular security audits are essential for identifying and mitigating potential vulnerabilities in TMG. Audits should include:
- Configuration Review:Verifying that TMG is configured according to best practices and security standards.
- Log Analysis:Examining event logs for suspicious activity and potential threats.
- Vulnerability Scanning:Identifying known vulnerabilities and implementing appropriate countermeasures.
- Penetration Testing:Simulating real-world attacks to assess the effectiveness of TMG’s security measures.
Final Wrap-Up: Threat Management Gateway
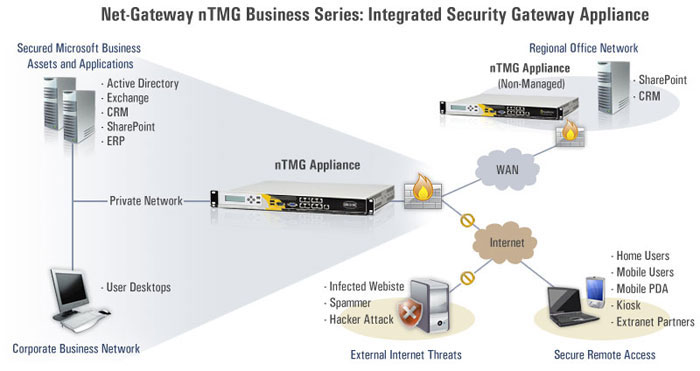
In conclusion, threat management gateway is a powerful tool that can help organizations to protect their networks from a wide range of threats. By implementing a TMG, organizations can improve their security posture and reduce the risk of a data breach.
Clarifying Questions
What is a threat management gateway?
A threat management gateway is a network security device that combines firewall, intrusion detection, and malware protection capabilities into a single, unified solution.
What are the benefits of using a threat management gateway?
Threat management gateways provide a number of benefits, including improved security, reduced risk of data breaches, and simplified management.
How do I deploy and configure a threat management gateway?
The specific steps for deploying and configuring a threat management gateway will vary depending on the product you choose. However, most TMGs will require you to install the software on a dedicated server and then configure the device to meet your specific security needs.
