The outward stock of foreign direct investment refers to the total value of investments made by a country’s residents in assets located in other countries. It is a measure of a country’s economic influence abroad and can provide insights into its economic development and global competitiveness.
This comprehensive guide will delve into the definition, measurement, determinants, and impact of the outward stock of foreign direct investment, providing a thorough understanding of this crucial aspect of international economics.
1. Definition of Outward Stock of Foreign Direct Investment: The Outward Stock Of Foreign Direct Investment Refers To
The outward stock of foreign direct investment (FDI) refers to the total value of investments made by a country’s residents in other countries. It includes equity investments, debt investments, and other forms of ownership and control over foreign assets.
2. Measurement of Outward Stock of Foreign Direct Investment
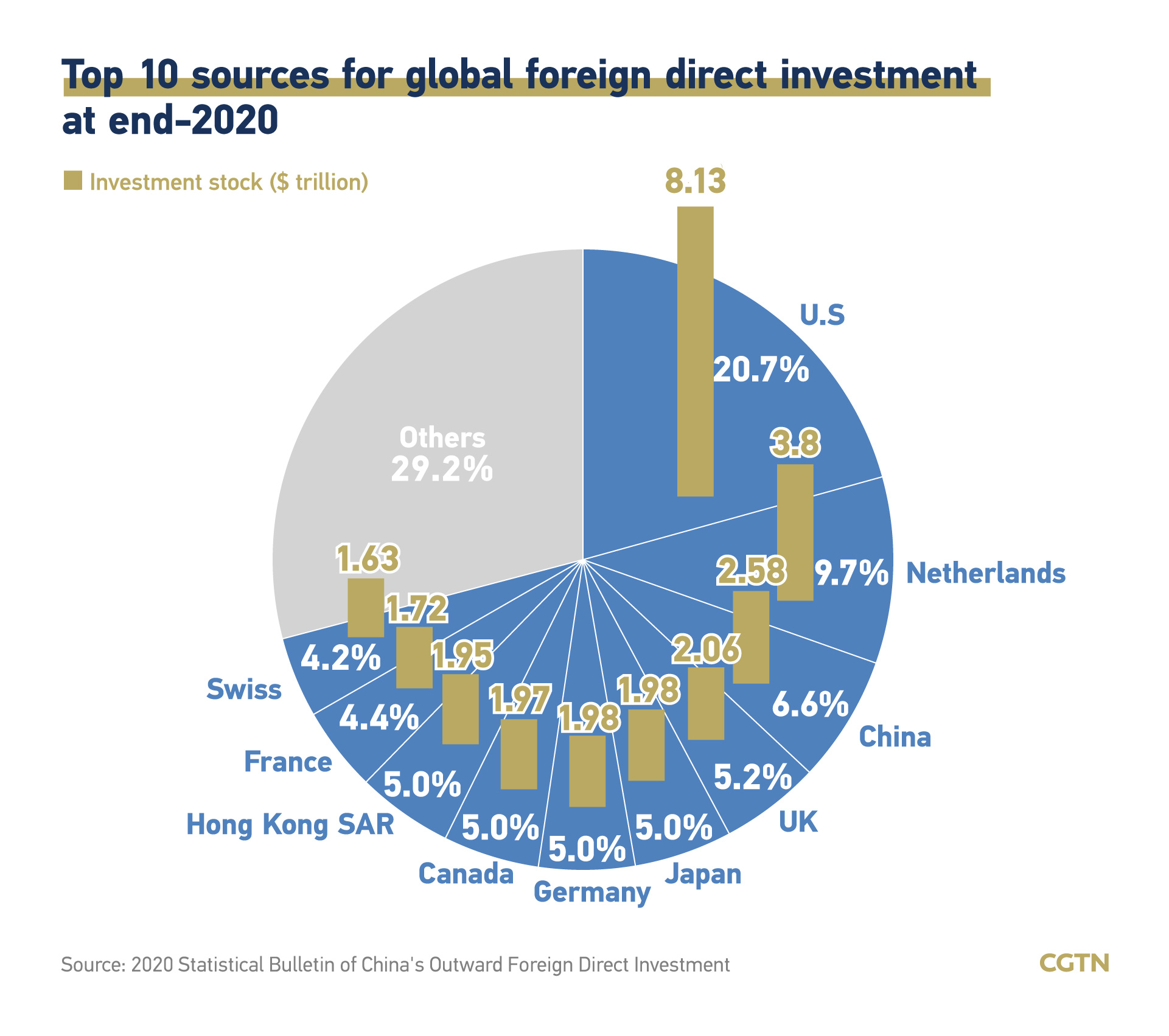
The outward stock of FDI is typically measured at the end of a specific period, such as a quarter or a year. It is calculated by summing the value of all foreign assets owned by residents of the country.
Challenges of Measuring Outward Stock of FDI
- Valuing foreign assets can be complex, especially for intangible assets such as intellectual property.
- Tracking investments made through intermediaries or shell companies can be difficult.
3. Determinants of Outward Stock of Foreign Direct Investment
Economic Factors
- Economic growth and stability in the host country
- Market size and potential
- Availability of skilled labor and infrastructure
Political Factors
- Political stability and rule of law
- Government policies and regulations
- Bilateral agreements and treaties
Social Factors
- Cultural proximity and language
- Education and skills of the population
- Consumer preferences and tastes
4. Impact of Outward Stock of Foreign Direct Investment
Positive Effects
- Increased economic growth and job creation in the host country
- Transfer of technology and knowledge
- Improved competitiveness of domestic firms
Negative Effects
- Potential loss of control over domestic industries
- Environmental degradation
- Exploitation of workers
5. Case Studies of Outward Stock of Foreign Direct Investment
China, The outward stock of foreign direct investment refers to
China has become a major source of outward FDI in recent years, with significant investments in sectors such as energy, infrastructure, and manufacturing.
The outward stock of foreign direct investment refers to the value of equity and capital invested by domestic investors in foreign countries. Determining what are good stocks to invest in right now requires careful consideration of factors such as industry trends, economic conditions, and company performance.
Understanding the outward stock of foreign direct investment can provide insights into global investment patterns and help inform investment decisions.
Japan
Japan has a long history of outward FDI, with investments primarily focused on Asia and the United States.
6. Trends in Outward Stock of Foreign Direct Investment
Global outward FDI has been growing steadily in recent years, driven by factors such as globalization, technological advancements, and the rise of emerging markets.
Emerging Trends
- Increasing investments in developing countries
- Growth of cross-border mergers and acquisitions
- Expansion of investment in sustainable and green technologies
Last Recap
In conclusion, the outward stock of foreign direct investment is a complex and multifaceted phenomenon that plays a significant role in the global economy. Understanding its determinants and impact is essential for policymakers, investors, and researchers alike.
FAQ Corner
What is the difference between inward and outward foreign direct investment?
Inward foreign direct investment refers to investments made by foreign residents in a country, while outward foreign direct investment refers to investments made by a country’s residents in other countries.
How is the outward stock of foreign direct investment measured?
The outward stock of foreign direct investment is typically measured using the historical cost method, which records the value of investments at the time they were made.
What are the main determinants of the outward stock of foreign direct investment?
The main determinants of the outward stock of foreign direct investment include economic growth, political stability, and trade policies.
