What is the distributive property in mathematics – Embark on a captivating exploration of the distributive property in mathematics, a fundamental concept that unveils the secrets of algebraic expressions and equations. Its simplicity belies its profound impact, transforming complex calculations into manageable steps.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of the distributive property, illuminating its applications in simplifying expressions, solving equations, and even factoring polynomials. Prepare to witness the elegance of mathematics as we unlock the mysteries of this indispensable tool.
Distributive Property in Mathematics: What Is The Distributive Property In Mathematics
The distributive property is a fundamental property in mathematics that describes the relationship between multiplication and addition (or subtraction). It plays a crucial role in simplifying algebraic expressions, solving equations, and factoring polynomials.
Distributive Property: Concept and Definition
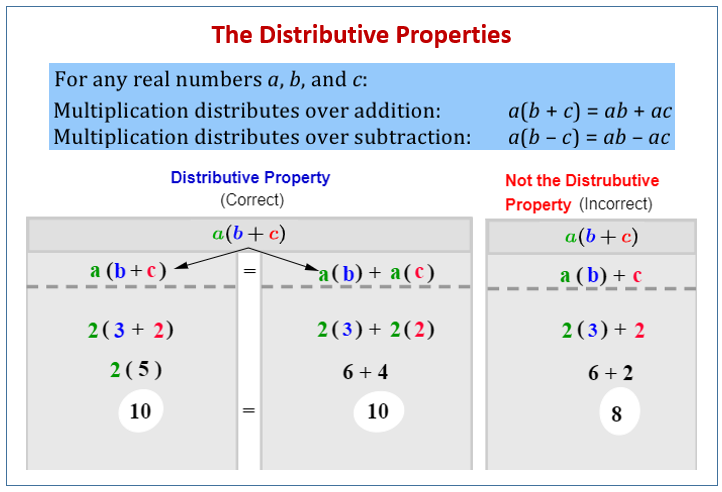
The distributive property states that the multiplication of a number (or variable) by the sum (or difference) of two other numbers (or variables) is equal to the sum (or difference) of the products of the first number (or variable) and each of the other numbers (or variables).
Algebraically, the distributive property can be expressed as:
a(b + c) = ab + ac
a(b
- c) = ab
- ac
Applications of the Distributive Property, What is the distributive property in mathematics
Simplifying Algebraic Expressions
The distributive property is used to simplify algebraic expressions by combining like terms. For example:
2(x + 3) = 2x + 6
The distributive property in mathematics is a fundamental property that states that the multiplication of a number by a sum is equal to the sum of the products of the number by each of the addends. This property is essential in various mathematical operations and applications, such as simplifying expressions, solving equations, and understanding the behavior of functions.
In the context of real estate, the distributive property can be applied to calculate the total cost of a property by considering the individual costs of land, construction, and other expenses. For example, if you are considering obtaining arizona real estate licenses , understanding the distributive property can help you determine the total cost of the licenses and associated fees.
Solving Equations
The distributive property is used to solve equations by isolating the variable on one side of the equation. For example:
3(x
- 2) = 15
- x
- 6 = 15
- x = 21
x = 7
Factoring Polynomials
The distributive property is used to factor polynomials by finding common factors. For example:
x2+ 2x + 1 = (x + 1) 2
Properties of the Distributive Property
Commutative Property
The distributive property is commutative, meaning that the order of the terms being added or subtracted does not affect the result. For example:
a(b + c) = a(c + b)
Associative Property
The distributive property is associative, meaning that the grouping of the terms being added or subtracted does not affect the result. For example:
a(b + (c + d)) = a((b + c) + d)
Distributive Property over Addition and Subtraction
The distributive property holds true for both addition and subtraction. That is:
a(b + c) = ab + ac
a(b
- c) = ab
- ac
Distributive Property and Real-World Examples
The distributive property finds applications in various fields, including physics, economics, and engineering. Here are some real-world examples:
- In physics, the distributive property is used to calculate the total force acting on an object. For example, if an object is subjected to three forces of 5 N, 10 N, and 15 N, the total force is 5 N + 10 N + 15 N = 30 N.
- In economics, the distributive property is used to calculate the total cost of goods or services. For example, if a store sells apples at $1 per pound and oranges at $2 per pound, the total cost of 3 pounds of apples and 2 pounds of oranges is $3 + $4 = $7.
- In engineering, the distributive property is used to calculate the total resistance of a circuit. For example, if a circuit has three resistors with resistances of 5 ohms, 10 ohms, and 15 ohms, the total resistance is 5 ohms + 10 ohms + 15 ohms = 30 ohms.
Epilogue
The distributive property stands as a cornerstone of mathematical operations, empowering us to navigate the complexities of algebra with ease. Its versatility extends beyond theoretical applications, reaching into the practical realm of everyday life. Whether in physics, economics, or engineering, the distributive property serves as a guiding light, illuminating the path to problem-solving success.
As we bid farewell to this mathematical odyssey, let us carry the knowledge of the distributive property with us, confident in its ability to simplify our mathematical endeavors and unlock the wonders of the quantitative world.
Popular Questions
What is the algebraic definition of the distributive property?
The distributive property states that for any real numbers a, b, and c, a(b + c) = ab + ac and (a + b)c = ac + bc.
How is the distributive property used in real-world scenarios?
The distributive property finds applications in various fields, including physics, economics, and engineering. For example, in physics, it is used to calculate the total force acting on an object.
