Strategic performance management system is a transformative tool that empowers organizations to align their operations with long-term goals, drive continuous improvement, and achieve卓越 operational excellence. By implementing a strategic performance management system, organizations can gain a competitive edge, enhance stakeholder value, and ensure sustainable growth.
This comprehensive guide delves into the intricacies of strategic performance management systems, providing a roadmap for successful design, implementation, and utilization. We will explore the key components, best practices, challenges, and case studies to equip you with the knowledge and insights necessary to harness the full potential of this powerful management approach.
Strategic performance management systems provide a comprehensive approach to evaluating and enhancing organizational performance. To further optimize this system, it is crucial to explore innovative investment opportunities, such as investing in private equity as a retail investor . By leveraging this strategy, organizations can gain access to a wider range of growth opportunities, fostering long-term success and reinforcing the effectiveness of their strategic performance management systems.
1. Overview of Strategic Performance Management Systems
Strategic performance management systems (SPMSs) are frameworks that align organizational performance with strategic goals. They provide a structured approach to measuring, evaluating, and improving performance to achieve desired outcomes.
Purpose and Benefits of SPMSs
- Align individual and organizational performance with strategic objectives
- Improve communication and collaboration across departments
- Identify and prioritize areas for improvement
- Enhance decision-making by providing data-driven insights
- Foster a culture of accountability and continuous improvement
Key Components of SPMSs, Strategic performance management system
- Strategic Goals:Clearly defined goals that align with the organization’s mission and vision
- Performance Measures:Key performance indicators (KPIs) that track progress towards strategic goals
- Performance Monitoring:Regular collection and analysis of performance data
- Performance Evaluation:Assessment of performance against targets and identification of areas for improvement
- Continuous Improvement:Development and implementation of plans to address performance gaps
2. Designing and Implementing Strategic Performance Management Systems
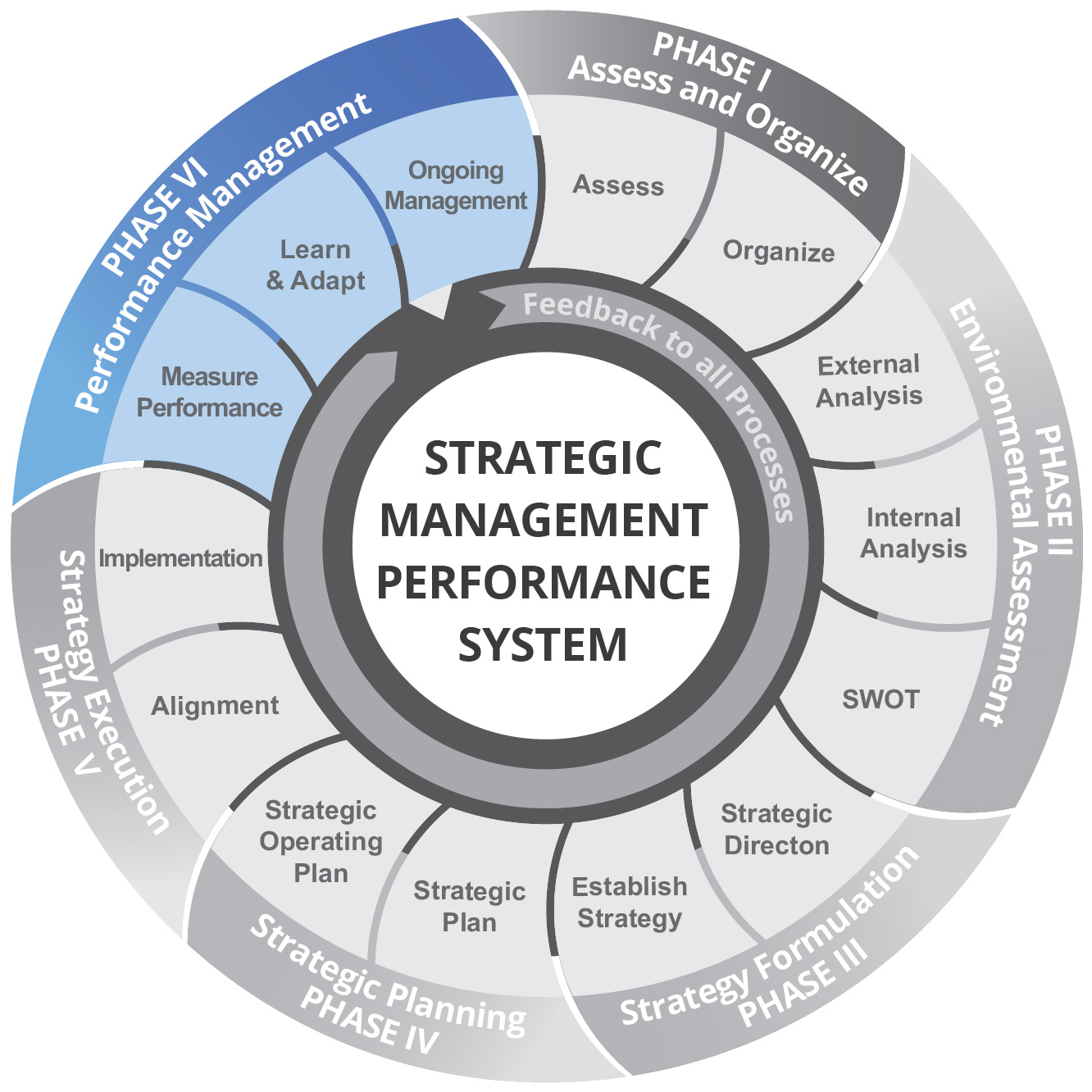
Step-by-Step Process
- Define Strategic Goals:Establish clear and measurable strategic goals
- Identify Key Performance Indicators:Select KPIs that align with strategic goals
- Involve Stakeholders:Engage key stakeholders in the design and implementation process
- Communicate Goals and Metrics:Cascade strategic goals and KPIs throughout the organization
- Establish Performance Targets:Set specific and challenging performance targets
- Monitor and Evaluate Performance:Track progress and identify areas for improvement
- Implement Improvement Plans:Develop and execute plans to address performance gaps
Importance of Stakeholder Involvement
- Ensures buy-in and support from all levels of the organization
- Identifies diverse perspectives and insights
- Fosters a sense of ownership and accountability
Best Practices for Communicating Strategic Performance Goals
- Use clear and concise language
- Communicate goals at all levels of the organization
- Provide context and rationale for goals
- Use visuals and storytelling to make goals relatable
3. Measuring and Evaluating Performance
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
- Quantitative measures that track progress towards strategic goals
- Should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART)
- Examples: Revenue growth, customer satisfaction, employee engagement
Methods for Collecting and Analyzing Performance Data
- Data Collection:Surveys, interviews, performance reviews, financial statements
- Data Analysis:Trend analysis, variance analysis, root cause analysis
Using Performance Data to Identify Areas for Improvement
- Identify performance gaps between actual and target values
- Analyze data to identify underlying causes of performance issues
- Prioritize areas for improvement based on impact and feasibility
4. Using Strategic Performance Management Systems to Drive Continuous Improvement
Identifying and Prioritizing Improvement Opportunities
- Use performance data to identify areas where performance falls short of expectations
- Analyze data to identify root causes of performance issues
- Prioritize improvement opportunities based on impact and feasibility
Developing and Implementing Improvement Plans
- Define specific and measurable improvement goals
- Identify resources and timelines for implementation
- Assign responsibilities and track progress regularly
Examples of Continuous Improvement
- Improving customer satisfaction through enhanced service delivery
- Reducing operational costs by optimizing processes
- Increasing employee productivity through training and development
5. Challenges and Best Practices in Strategic Performance Management
Common Challenges
- Lack of Stakeholder Involvement:Failure to engage stakeholders can lead to resistance and lack of ownership
- Poor Communication:Inadequate communication of strategic goals and performance expectations can result in confusion and misalignment
- Unclear Performance Measures:KPIs that are not clearly defined or aligned with strategic goals can lead to ineffective measurement
Best Practices for Overcoming Challenges
- Engage Stakeholders:Involve key stakeholders in all phases of SPMS design and implementation
- Communicate Effectively:Clearly communicate strategic goals, performance expectations, and progress updates
- Use SMART KPIs:Define KPIs that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound
Case Studies of Successful Implementations
- Example 1:Company X implemented a SPMS that aligned performance with customer satisfaction goals, resulting in a significant increase in customer loyalty
- Example 2:Company Y used a SPMS to identify and address operational inefficiencies, leading to a reduction in costs and improved profitability
Ultimate Conclusion
In conclusion, strategic performance management system is not merely a collection of metrics and processes; it is a dynamic and iterative journey that requires commitment, collaboration, and a relentless pursuit of excellence. By embracing the principles Artikeld in this guide, organizations can unlock their true potential, achieve lasting success, and make a meaningful impact in their respective industries.
FAQ
What are the key benefits of implementing a strategic performance management system?
Strategic performance management systems offer numerous benefits, including improved alignment with strategic goals, enhanced decision-making, increased accountability, and a culture of continuous improvement.
How do you measure the effectiveness of a strategic performance management system?
The effectiveness of a strategic performance management system can be measured by assessing its impact on key performance indicators (KPIs), stakeholder satisfaction, and overall organizational performance.
What are some common challenges in implementing a strategic performance management system?
Common challenges include resistance to change, lack of stakeholder involvement, and difficulty in cascading strategic goals throughout the organization. However, with proper planning and communication, these challenges can be overcome.
