The average annual return from stock investments historically is – The average annual return from stock investments historically has captured the attention of investors and financial experts alike. This comprehensive guide delves into the historical performance of stock markets, providing insights into the factors that have influenced returns, the relationship between market performance and volatility, and the implications for long-term investment strategies.
As we navigate the complexities of the stock market, understanding historical returns is crucial for informed decision-making. This guide will equip you with the knowledge and tools to assess risk and return, manage volatility, and harness the power of diversification to maximize your investment potential.
Historical Stock Return Overview
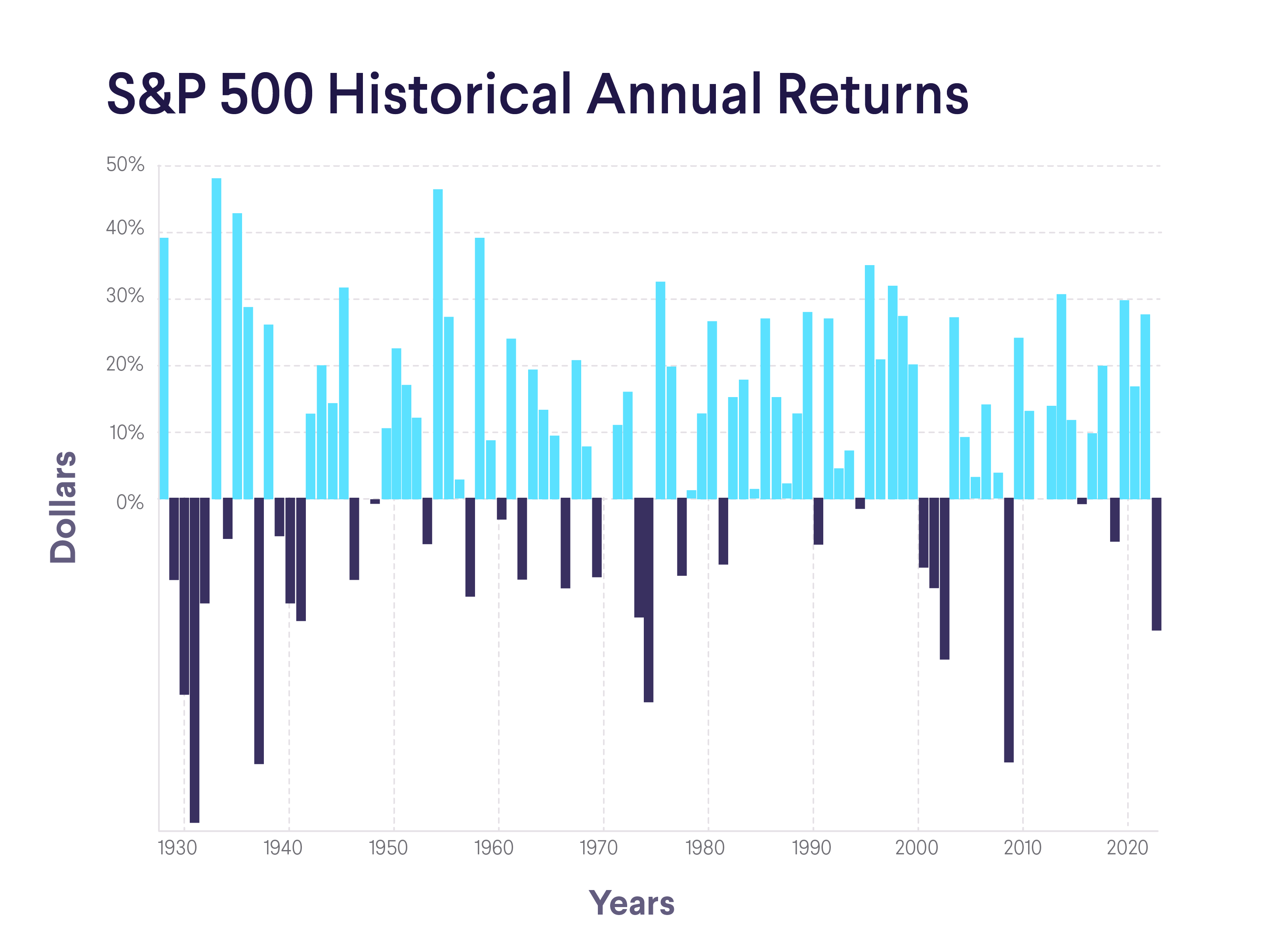
The average annual return from stock investments historically has been a topic of significant interest for investors and financial professionals. Understanding historical stock returns can provide valuable insights into the potential performance of stock investments over time, helping investors make informed investment decisions.
Factors that influence historical stock returns include economic growth, inflation, interest rates, and geopolitical events. Over the long term, stock returns have generally outpaced inflation, making them a valuable asset class for building wealth.
Examples of Historical Stock Market Returns
- From 1926 to 2022, the S&P 500 index, a widely recognized benchmark for the US stock market, delivered an average annual return of approximately 10%.
- The FTSE 100 index, a measure of the performance of the UK stock market, has historically returned around 5% annually since its inception in 1984.
- The Nikkei 225 index, a key indicator of the Japanese stock market, has experienced periods of both high and low returns, with an average annual return of approximately 7% over the past several decades.
Market Performance and Volatility
The performance of the stock market is closely tied to economic conditions. During periods of economic growth, corporate profits tend to increase, leading to higher stock prices and returns. Conversely, during economic downturns, corporate profits may decline, resulting in lower stock prices and returns.
Geopolitical events can also significantly impact stock market returns. Wars, political instability, and natural disasters can create uncertainty and volatility in the markets, leading to fluctuations in stock prices.
Volatility and Risk Tolerance
Volatility refers to the degree of price fluctuations in the stock market. Higher volatility indicates greater price swings, which can be both a source of opportunity and risk for investors.
Investors with a higher risk tolerance may be more comfortable with volatile markets, as they have the potential to generate higher returns. However, investors with a lower risk tolerance may prefer to invest in less volatile assets.
Risk and Return Relationship
In the world of investing, there is a fundamental relationship between risk and return. Higher-risk investments generally offer the potential for higher returns, while lower-risk investments typically provide lower returns.
Historically, the average annual return from stock investments has been around 10%. However, there are other investment options that can potentially offer higher returns, such as real estate. If you’re interested in learning how to invest in real estate with no money, there are a number of resources available online.
Here’s one that can help you get started. Despite the potential for higher returns, it’s important to remember that all investments carry some level of risk. Be sure to do your research and understand the risks involved before investing any money.
Historical stock returns can help investors assess the risk of different stock investments. Stocks with a history of high volatility may be considered riskier than those with a history of low volatility.
Managing Risk and Maximizing Returns
Investors can employ various strategies to manage risk and maximize returns in stock investments. These strategies include:
- Diversification: Spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and companies to reduce overall portfolio risk.
- Dollar-cost averaging: Investing a fixed amount of money in a stock or fund at regular intervals, regardless of the market price.
- Value investing: Investing in stocks that are trading at a discount to their intrinsic value.
Long-Term Trends and Patterns: The Average Annual Return From Stock Investments Historically Is
Examining historical stock returns over extended periods can reveal long-term trends and patterns. These trends can provide insights into the cyclical nature of the stock market and help investors make informed long-term investment decisions.
Factors that contribute to long-term trends include technological advancements, demographic changes, and global economic conditions.
Using Historical Data for Long-Term Decisions
Investors can use historical stock return data to identify long-term investment opportunities. By understanding the historical performance of different asset classes and investment strategies, investors can make informed decisions about how to allocate their portfolios for the long term.
Inflation and Historical Stock Returns
Inflation is a general increase in prices and a decrease in the purchasing power of money. Inflation can erode the value of stock returns over time, as the purchasing power of the returns decreases.
Strategies to Mitigate Inflation
Investors can employ several strategies to mitigate the impact of inflation on their stock investments:
- Investing in inflation-protected securities: These securities are designed to protect against the effects of inflation by adjusting their principal value based on inflation.
- Investing in companies with pricing power: Companies with strong brands and pricing power can pass on inflation-related cost increases to their customers, protecting their profit margins.
Diversification and Historical Stock Returns
Diversification is a risk management strategy that involves spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and companies. Diversification can reduce the overall risk of a portfolio by reducing the impact of any single investment’s performance.
Benefits of Diversification, The average annual return from stock investments historically is
- Reduced risk: Diversification helps reduce the risk of losing money due to the poor performance of a single investment or asset class.
- Enhanced returns: Diversification can potentially enhance returns by combining investments with different risk and return characteristics.
Global Stock Market Returns
Global stock markets exhibit different performance characteristics based on economic conditions, political stability, and currency fluctuations. Comparing and contrasting historical stock returns in different global markets can provide insights into the potential opportunities and risks of investing internationally.
Implications for Investors
Understanding global stock market returns can help investors make informed decisions about diversifying their portfolios internationally. By investing in a mix of global markets, investors can potentially reduce risk and enhance returns.
Data Sources and Methodologies
Reliable data sources for historical stock returns include:
- Bloomberg
- Reuters
- Yahoo Finance
Methodologies used to calculate average annual returns typically involve compounding the annual returns over the specified period.
Limitations and Biases
Historical stock return data may be subject to certain limitations and biases, including:
- Survivorship bias: This bias occurs when only the returns of surviving companies are considered, excluding companies that have gone bankrupt or delisted.
- Data availability: Historical stock return data may not be available for all companies or time periods.
Applications and Implications
Historical stock returns have numerous applications for investors, analysts, and policymakers:
- Investment decision-making: Investors use historical stock returns to assess the potential risk and return of different investment strategies.
- Performance evaluation: Analysts use historical stock returns to evaluate the performance of investment managers and funds.
- Policymaking: Policymakers use historical stock returns to inform decisions related to economic growth, inflation, and financial regulation.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the average annual return from stock investments historically provides valuable lessons for investors seeking to navigate the ever-evolving financial landscape. By understanding the factors that have shaped historical returns, investors can make informed decisions, manage risk effectively, and position themselves for long-term success.
Remember, investing in stocks involves both potential rewards and risks. Careful research, diversification, and a long-term perspective are essential for maximizing your chances of achieving your financial goals.
FAQ Insights
What factors influence historical stock returns?
Economic growth, interest rates, inflation, geopolitical events, and company earnings are among the key factors that impact historical stock returns.
How can historical stock returns help investors assess risk?
Historical returns provide insights into the potential volatility and risk associated with stock investments, allowing investors to make informed decisions about their risk tolerance.
What are the benefits of diversification in stock investments?
Diversification reduces risk by spreading investments across different asset classes, industries, and geographic regions, enhancing the overall stability of a portfolio.
