Where do short term investments go on a balance sheet – Where do short-term investments go on a balance sheet? This question delves into the intriguing realm of accounting and financial reporting, where the intricacies of balance sheet classification and valuation come into play. Embark on this journey to uncover the secrets of short-term investments and their impact on a company’s financial well-being.
Short-term investments, as the name suggests, are highly liquid assets held by a company for a period of less than one year. Examples of such investments include marketable securities, treasury bills, and commercial paper. These investments serve as a temporary parking spot for excess cash, providing companies with flexibility and the potential for short-term gains.
Short-Term Investments on Balance Sheet
Short-term investments are highly liquid financial assets that can be easily converted into cash within a year or less. These investments are held by companies to maintain excess cash, preserve capital, and generate income.
Examples of Short-Term Investments
- Cash equivalents (e.g., money market accounts, treasury bills)
- Short-term government bonds
- Commercial paper
- Certificates of deposit (CDs)
- Short-term corporate bonds
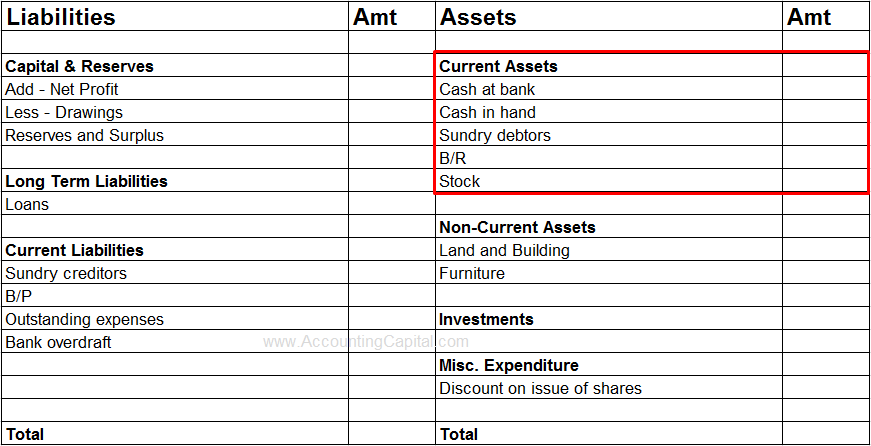
Balance Sheet Classification
Short-term investments are classified as current assets on the balance sheet. They are typically reported in the “marketable securities” line item under the “current assets” section.
Accounting Treatment, Where do short term investments go on a balance sheet
Short-term investments are initially recorded at cost. Subsequent changes in their fair value are recognized in the income statement through the unrealized gain or loss account. When these investments are sold, the difference between the sale proceeds and the carrying value is recognized as a realized gain or loss.
Financial Statement Analysis
Short-term investments can impact financial ratios, such as the current ratio and quick ratio. A high proportion of short-term investments can improve liquidity but may also indicate a lack of profitable investment opportunities.
The holding of short-term investments can also affect profitability. Income generated from these investments can contribute to the company’s overall profitability. However, the level of return on short-term investments may vary depending on market conditions.
Short term investments, which are highly liquid assets that can be easily converted into cash, are typically reported as current assets on a balance sheet. Understanding where these investments are placed can help investors make informed decisions about their financial strategies.
One such strategy is choosing between a Roth IRA and a traditional IRA. Both options offer tax benefits, but the choice depends on individual circumstances. To explore this topic further, I recommend visiting should i invest in roth ira or traditional ira for valuable insights.
Reporting and Disclosure
The reporting of short-term investments in financial statements follows specific guidelines. The following table summarizes the key reporting requirements:
| Item | Description |
|---|---|
| Marketable Securities | Short-term investments reported at fair value |
| Unrealized Gain (Loss) | Changes in fair value recognized in income statement |
| Realized Gain (Loss) | Difference between sale proceeds and carrying value |
In addition to the reporting requirements, companies are also required to disclose information about their short-term investments. This includes:
- The nature and amount of short-term investments
- The basis of valuation
- Any restrictions or encumbrances on the investments
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, understanding the classification and accounting treatment of short-term investments is crucial for accurate financial reporting and analysis. These investments play a significant role in shaping a company’s liquidity, profitability, and overall financial health. By carefully managing short-term investments, companies can optimize their financial resources and position themselves for long-term success.
Popular Questions: Where Do Short Term Investments Go On A Balance Sheet
What is the definition of a short-term investment?
A short-term investment is a highly liquid asset held by a company for a period of less than one year, with the primary purpose of generating short-term gains or maintaining liquidity.
Where are short-term investments reported on the balance sheet?
Short-term investments are typically reported as a line item under the current assets section of the balance sheet, indicating their high liquidity and short-term nature.
How are short-term investments valued?
Short-term investments are typically valued at fair market value, which reflects the current market price of the investment. This valuation method ensures that the balance sheet accurately reflects the current financial position of the company.
